How LiDAR is Transforming the Safety of Construction Sites
Learn how 3D LiDAR technology contributes to a significant increase in construction site safety.
Working on construction sites is hazardous by nature.
Every year, hundreds of construction workers are injured as a result of hazardous working conditions. For example, despite employing only 6% of American workers, the construction industry is responsible for nearly 20% of worker fatalities nationwide.
This disparity highlights the importance of ongoing initiatives to improve workplace safety for those working in the construction industry. Fortunately, this is where LiDAR technology shines, enabling previously unattainable possibilities and saving lives.
Continue reading to find out more about how LiDAR is changing the safety and operations at construction sites.
What makes LiDAR data valuable?
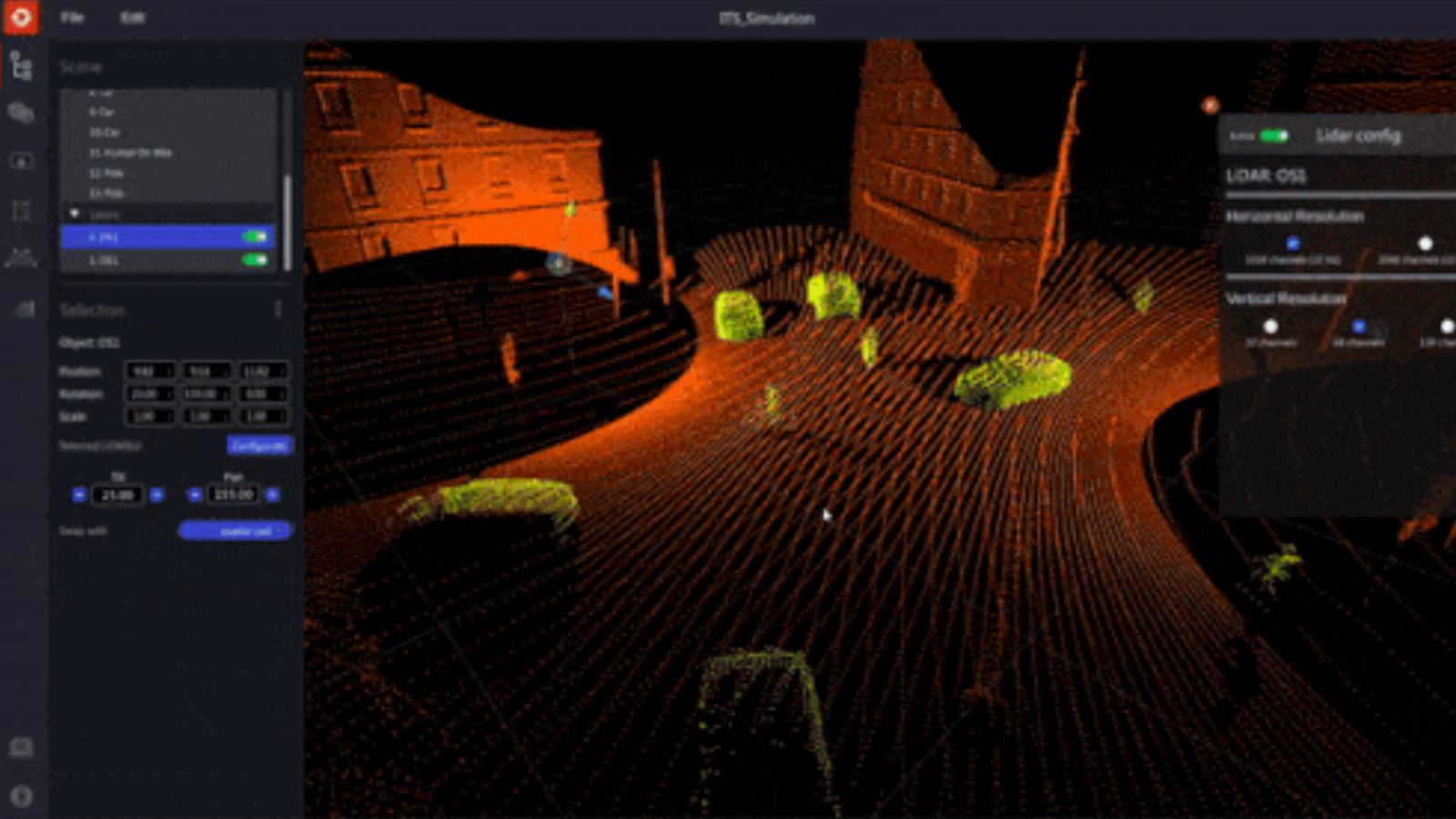
The ability of LiDAR to generate very precise, comprehensive 3D photographs of the immediate surroundings in any lighting situation is one of its major advantages.
These photos are subsequently analyzed and saved as datasets, which can essentially take one of two forms:
In real-time: that is, the data is immediately put to use, such as when raising an alarm after a risky incident;
Aggregated over time: insightful statistical measures are obtained over time using the data. For instance, to comprehend where and when these types of occurrences are occurring.
Advantages of LiDAR for Safety in Construction
Working on a construction site is inherently risky, as we've already mentioned. There is no way to entirely remove all risk, even if every worker on the job site adheres to all safety rules and best practices.
But, there are several rather obvious ways in which construction site safety may be enhanced and the repercussions significantly reduced with the use of LiDAR.
Below are the top four advantages:
- Worker's safety through Object Detection
- Accurate Site Mapping
- Project simulations
- Quality control in construction
Object detection for improving worker safety
Another important benefit of LiDAR is its capacity to reduce the risk of worker death on building sites.
LiDAR's ability to spot dangers and obstacles that people would miss in the absence of visual or auditory signals makes this possible.
The Augmented LiDAR Software is currently being used by a client to analyze data from a LiDAR sensor mounted on a crane to detect hazardous situations and potential collisions with workers and machinery. This exemplifies the effective implementation of a safety measure.

Due to the possibility that the load, rather than only the crane itself, may be the cause of the collision, this application allows for the dynamic adaptation of the safety zones determined by the location of the block and the shape of the load.
A person entering the safety zone will set off an alert.
The same idea holds true for LiDARs deployed in mobile heavy equipment as well as infrastructure-based machinery like cranes.
The generally difficult terrain seen in these scenarios does not result in false alarms since the LiDAR sensor interprets the world in three dimensions.
Accurate Site Mapping
The compilation of precise floor plans and site maps, as well as more recently, the fabrication of a Digital Twin, is one of the most significant advantages of LiDAR in the construction industry.
Historically, manual mapping and surveying equipment like 2D LiDAR scanners and, more recently, photogrammetric technology have been used for this. In practice, both approaches are typically time-consuming and frequently lead to discrepancies in the mapped data.
A 3D LIDAR system, in contrast, is made to produce several light beams in order to capture more detailed object data as contrasted to a 2D LIDAR system, which directs just one light beam towards a surface. By moving to 3D LiDAR, site mapping may be completed with a great deal less time and effort while also improving the quality of the data being gathered.
For instance, you may quickly create a point-cloud 3D map and get an accurate view of your location utilizing Outsight's LiDAR preprocessing software.

Project Simulations (or ‘Virtual Reality’ setups)
In this application, the 3D LiDAR serves as the foundation for a comprehensive building project simulation.
Besides from modeling, the 3D LiDAR can also record how the dynamic aspect of the environment changes, whether it does so slowly (such as when analyzing a stockpile's progression over days) or fast (such as when moving workers and equipment).
As a result, project managers may have a better idea of how the project will look in reality during the development phase.
In one deployment, the simulation tool was used to create specific scenarios and evaluate the efficacy of 3D LiDAR systems in a variety of settings to cover all potentially hazardous situations.


Quality Control (QC) in Construction
Conventional paper-based quality control is typically a time-consuming and expensive process.
One such methodology makes use of vision-based techniques, where the main step is taking digital photos on the spot and linking them to the 3D CAD models.
After that, a quality control check is performed to find any differences by comparing the digital pictures from the site to the CAD models.
These methods are now being superseded by 3D models, which use three matching reference points to identify 3D items using laser scans and superimpose them on project 3D CAD models.

Conclusion
Construction sites are inherently dangerous places, but LiDAR technology makes it possible to reduce the risk of accidents while still meeting project deadlines.
There are various ways that LiDAR is revolutionizing construction site safety, from worker safety to automated mapping solutions to 3D reconstruction and modeling to risk management.

Sources
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
LiDAR INSIGHTER Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.